Graph Assignment 3 - CH34 MONETARY POLICY AND FISCAL POLICY
a. If the Bank of Korea raises its Base Rate, it would mean the decrease of money supply. According to the liquidity preference theory, the interest rate adjusts to balance the supply of and demand for money. Therefore, the decrease in the money supply (MS₁ to MS₂) would lead to the increase of the equilibrium interest rate (r₁ to r₂). (Graph below)

b. In the short-run, output falls from Y₁ to Y₂ and the price level falls from P₁ to P₂.
Explanation: Since the interest rate is the cost of borrowing, the increase in interest rates discourages investment spending, thus lowering the quantity of goods and services demanded at each price level. This will cause the aggregate-demand curve to shift to the left (AD₁ to AD₂). In the short run, the economy will move from point A to point B. Output falls from Y₁ to Y₂ and the price level falls from P₁ to P₂. (Graph below)
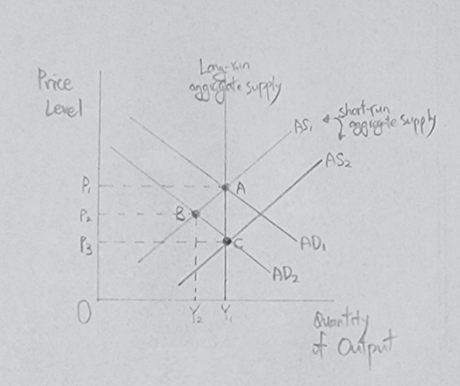
c. When the economy makes the transition from its short-run equilibrium to its new long-run equilibrium, the price level falls to P₃.
Explanation: Over time, as the expected price level adjusts, the short-run aggregate-supply curve will shift to the right from AS₁ to AS₂. Consequently, the economy will reach point C, where the new aggregate-demand curve crosses the long-run aggregate-supply curve. Therefore, the price level falls to P₃ and output returns to it natural level Y₁. (Graph above)
d. As the price level is one determinant of the quantity of money demanded, decrease in the price level will lead to the decrease of money demand. Therefore, the decrease in the price level (P₁ to P₃) shifts the money demand curve to the left (MD₁ to MD₃), causing the interest rate to drop from r₂ to r₃. (Graph below)
